Introduction
Copyright statements are critical tools for business owners aiming to safeguard their creative works and intellectual property. More than just symbols or phrases, these statements clearly communicate ownership, legal protections, and usage terms — reducing risks of unauthorized use and disputes. This guide unpacks the fundamental elements every copyright statement must contain, explores the relevant legal implications and protection durations, clarifies usage restrictions and permissions, highlights their vital role in digital and published media, and demonstrates how they clarify ownership and protection status. Understanding these chapters equips business owners with the knowledge to confidently protect their valuable content and reinforce their brand’s legal standing.
Tables des matières
Chapter 1: Fundamental Elements of a Copyright Statement
- Essential Components of a Copyright Statement: Symbol, Date, and Ownership
- Navigating Fair Use and Legal Boundaries Within Copyright Statement Elements
- Clarifying Ownership and Protection: The Essential Components of a Copyright Statement
Chapter 2: Legal Implications and Duration in Copyright Statements
- Navigating Legal Protections and Liability Risks in Copyright Statements
- Navigating Global Copyright Durations and Legal Variations in Copyright Statements
- Navigating Fair Use and Licensing Restrictions Within Copyright’s Legal Framework
Chapter 3: Usage Restrictions and Permissions in Copyright Statements
- Navigating Fair Use and Fair Dealing: Legal Boundaries Embedded in Copyright Statements
- Harnessing Creative Commons Licenses: Balancing Permissions and Restrictions in Copyright Statements
- Navigating Public Domain and Government Works: Key to Usage Rights in Copyright Statements
Chapter 4: Copyright Statement Roles in Digital and Published Media
- Integrating Technology and Legal Frameworks to Safeguard Copyright in Modern Media
- Economic Impact and Enforcement Challenges of Copyright Statements Across Media Platforms
- Navigating Society and Global Power: The Far-Reaching Effects of Copyright Statements
Chapter 5: Clarifying Ownership and Protection Status through Copyright Statements
- Leveraging Technology to Strengthen Ownership Clarity and Protection in Copyright Statements
- Economic Impact of Copyright Statements: Protecting Creative Industries and Encouraging Innovation
- Navigating the Legal Authority and Societal Impact of Copyright Statements
Chapter 1: Fundamental Elements of a Copyright Statement

1. Essential Components of a Copyright Statement: Symbol, Date, and Ownership
A copyright statement serves as a clear, concise declaration of legal ownership over a creative work. It typically comprises three core components that together assert the claim: the copyright symbol ©, the year of first publication, and the name of the copyright owner. These elements are fundamental because they provide unmistakable evidence of when the work was made available and who holds its rights.
The copyright symbol © acts as an internationally recognized alert that the work is protected under copyright law. While its use is not strictly mandatory in all jurisdictions, its inclusion helps communicate ownership visibly and deters unauthorized use. This symbol evolved primarily within U.S. legislation as a straightforward visual marker signaling legal protection.
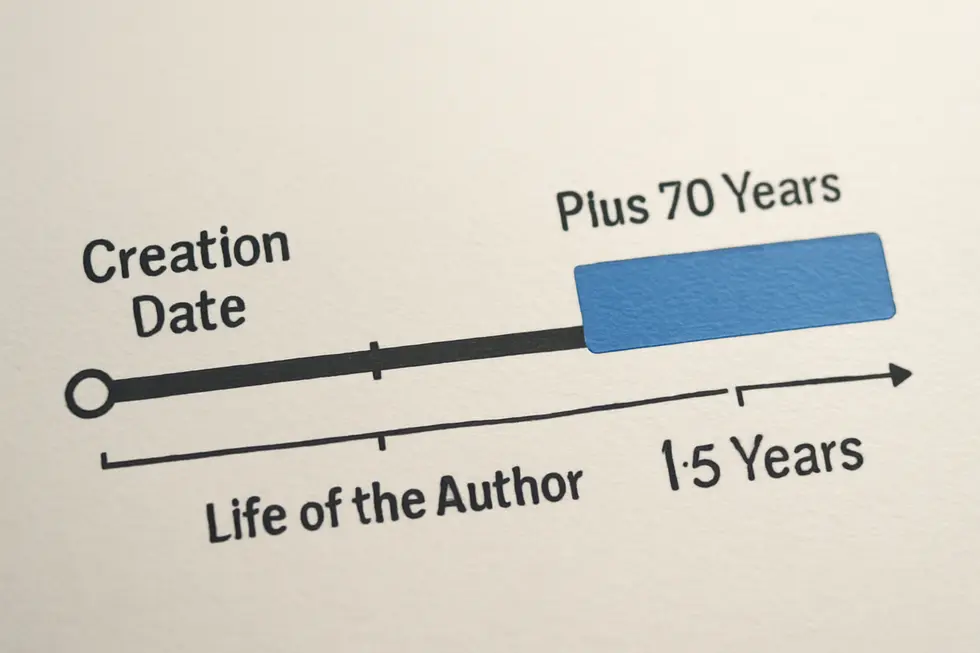
Following the symbol, the publication year anchors the copyright in time. Stating when the work was first published is crucial because copyright protection spans a specific duration starting from this date—commonly, the author’s lifetime plus 70 years. This date also assists in identifying the relevant legal framework applicable at the time of release.
Lastly, the owner’s name identifies the individual or entity entitled to enforce copyright rights. Naming the owner not only clarifies who controls the usage and licensing of the work but also supports enforcement actions by establishing clear legal standing.
Together, these elements comprise a format typically seen as: © [Year] [Owner Name], for example, © 2025 Jane Doe. This format provides an immediate understanding of ownership and protection status without ambiguity. It also plays a vital role in minimizing disputes and strengthening enforcement by marking the work unmistakably as the intellectual property of a defined party.
For those seeking further guidance on crafting copyright notices, resources such as this detailed guide offer practical advice and examples. Additionally, clarifying how these elements fit within broader intellectual property protection strategies can be found in comprehensive discussions on copyright protection for creative works.
2. Navigating Fair Use and Legal Boundaries Within Copyright Statement Elements
A copyright statement serves as a clear notice of ownership, but its impact extends deeper when considered alongside the legal context, particularly the doctrine of fair use. While the fundamental elements—a copyright symbol (©), the year of first publication, and the owner’s name—assert exclusive rights, they exist within a framework that carefully balances these rights against legally permitted exceptions.
Fair use allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission, depending on factors like purpose, nature, amount used, and effect on the work’s market value. This means a copyright statement is never an absolute barrier; it communicates rights held but implicitly recognizes that certain uses, such as educational or transformative purposes, may be lawfully exempt. For instance, a work marked © 2025 Jane Doe signals protection but does not automatically prevent fair use in commentary or critique.
In drafting copyright statements, clarity about reserved rights and permitted exceptions can reduce disputes. They often specify the scope of rights retained, such as reproduction or distribution, while acknowledging that fair use or other exceptions apply. Especially in complex business dealings involving copyright assignments, precisely defining which rights are transferred or retained underscores the interplay between ownership claims and legal limits.
Thus, a copyright statement is intrinsically connected to the broader legal environment. It not only marks the work as protected but also functions alongside fair use doctrines that shape enforcement and permitted use. Understanding this relationship enhances the statement’s role as an effective tool for communication and protection.
For more on fair use considerations in copyright, see this detailed analysis on understanding fair use in the age of generative AI.
3. Clarifying Ownership and Protection: The Essential Components of a Copyright Statement
A copyright statement serves as a clear and concise declaration that communicates essential information about a work’s legal protection. Its fundamental components—comprising the copyright symbol (©), the year of first publication, and the name of the copyright owner—perform distinct yet interrelated functions that establish transparency and guidance for users.
The © symbol acts as a universal indicator that the work is subject to copyright law. Its presence immediately signals to viewers that the content enjoys legal protection and that unauthorized reproduction or use is prohibited without proper authorization. This visual cue is widely recognized and thus plays a central role in deterring infringement.
Including the year of first publication provides a critical temporal reference. It marks when copyright protection commenced, which is vital because copyright duration depends on this date and varies depending on the legal context. By stating the year, the copyright statement offers users a clearer understanding of how long the work is protected and when it might enter the public domain. This insight is especially important for digital content, where reproductions can spread rapidly.
Equally important is the identification of the copyright holder through their name or an accepted abbreviation. This element precisely specifies to whom the exclusive rights belong and who should be contacted regarding licensing or permissions. It promotes proper attribution and supports enforcement efforts where unauthorized use occurs.
Together, these elements provide transparency, reduce ambiguity, and protect both the rights holder and the user community by clarifying legal ownership and protection status upfront. In digital media, embedding these details alongside tools like watermarks or metadata further enhances security and traceability.
For a more detailed discussion of copyright’s protective scope and its practical applications, the article on copyright protection for books, movies, and songs offre des informations précieuses.
Chapter 2: Legal Implications and Duration in Copyright Statements
1. Navigating Legal Protections and Liability Risks in Copyright Statements
A copyright statement serves as a vital legal instrument that notifies users of a work’s ownership and the protections afforded by copyright law. Central to this role is the legal framework that enforces these rights through both civil and criminal avenues. Civil law empowers copyright holders to pursue claims for unauthorized use, seeking damages that can be either actual losses or statutory amounts preset by legislation. Courts may also issue injunctions to immediately halt infringing activities, underscoring the seriousness of unauthorized reproduction or distribution.
Criminal consequences arise typically when infringement is intentional and conducted for commercial advantage. Penalties can range from substantial fines to imprisonment, emphasizing the deterrent role the law plays against willful violations. This dual approach balances protecting creators’ interests with penalizing those who knowingly flout copyright protections.
Copyright duration prominently influences the statement’s content and scope. Commonly, the protection extends through the author’s lifetime plus seventy years, though variations exist by jurisdiction or for corporate-owned works. Upon expiration, rights lapse and the work enters the public domain, becoming free for public use without infringement concerns. A clear declaration of these rights and durations within the statement helps prevent disputes and clarifies lawful usage.
Special considerations apply to different licensing scenarios such as open-source software, where violating terms immediately revokes granted permissions, potentially triggering swift legal action and loss of usage rights. Additionally, laws like the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) impose strict penalties for ignoring takedown requests, which can escalate rapidly, including large statutory fines and legal contempt charges.
Thus, copyright statements encapsulate a complex legal ecosystem, offering precise ownership claims and setting boundaries that protect creativity while outlining the risks and remedies for infringement. For a deeper insight into consequences following copyright law breaches, see Aaron Hall’s detailed explanation.
For businesses concerned with broader intellectual property protections, understanding the nuances discussed in this chapter complements strategies found in resources about copyright protection for creative works.
2. Navigating Global Copyright Durations and Legal Variations in Copyright Statements
Copyright statements act as crucial markers indicating legal rights, but their implications extend beyond simple ownership. Internationally, copyright durations vary, shaped by treaties and local laws. Most countries follow standards set by the Berne Convention, which mandates protection lasting the life of the author plus at least 50 years. Many nations, including Belgium and Uruguay, extend this to life plus 70 years, while others such as Belize and Zambia maintain shorter terms of life plus 50 years. These differences can impact how long a work is protected and determines when it enters the public domain.
The Universal Copyright Convention (UCC) complements Berne by setting a minimum protection standard of the author’s life plus 25 years, requiring formal copyright notices on published copies. The UCC’s provisions, such as shorter protection for photographic works, highlight how varied terminologies and thresholds affect copyright assertions globally.
Country-specific rules add complexity. The United States, for instance, sets a standard term of life plus 70 years for individuals but offers extended durations for anonymous or corporate works—generally up to 95 years after publication or 120 years from creation, whichever is shorter. Venezuela applies a life plus 60 years term, with specialized rules for audiovisual content. At the other extreme, Yemen enforces shorter protections, generally life plus 30 years, and specific governmental claims may apply post-term.
These varying norms influence the legal meaning behind copyright statements regarding a work’s protection status and enforcement. Jurisdictional nuances affect penalties for infringement and exceptions. For content platforms operating worldwide, adhering simultaneously to frameworks such as the U.S. DMCA and European Union directives is essential to managing legal risks and respecting rights across borders.
Understanding these international duration standards and legal differences is vital for correctly interpreting and applying copyright statements. This awareness supports content creators and users in navigating the global landscape of intellectual property protection while clarifying ownership and usage rights.
For more insights on copyright basics and legal nuances, see this resource on basics of copyright law.
Reference: List of copyright duration by country
3. Navigating Fair Use and Licensing Restrictions Within Copyright’s Legal Framework
A copyright statement goes beyond merely marking ownership; it signals the boundaries of lawful use, incorporating complexities like fair use and licensing restrictions that influence how protected works may be used. Fair use, a critical legal doctrine under U.S. law, permits limited unauthorized use of copyrighted material for purposes such as commentary, education, and research. This exception reflects a careful legal balance: it safeguards creators’ rights while ensuring public access to knowledge and culture.
When considering fair use, courts weigh factors including the purpose of use—favoring transformative, educational, or noncommercial purposes—the nature of the original work, the amount used, and the potential impact on the market for the original. These assessments are subtle and case-specific, meaning that what qualifies as fair use in one instance may not in another.
Licensing agreements layer additional, explicit conditions on how a work may be used, often including nondisclosure, non-compete, or termination clauses. These contractual terms establish precise legal boundaries that complement statutory protections, making compliance essential to avoid infringement claims beyond fair use allowances.
Furthermore, the temporal scope of copyright protection strongly affects these dynamics. Typically lasting the life of the author plus seventy years, copyright duration ensures economic and moral rights during the term but eventually expires, placing works into the public domain. At that point, licensing and fair use considerations cease, granting freedom to use the work without restriction.
By integrating clear fair use principles and explicit licensing terms within copyright statements, rights holders provide legal clarity and manage user expectations effectively. Such nuanced legal communication is vital to both upholding creative ownership and enabling socially important uses.
For additional insight on copyright licensing, see the ETB Law Guide to Copyright Licensing: https://www.etblaw.com/guide-to-copyright-licensing/ and explore how to safeguard your creative works with comprehensive protection at Benefits of Copyright Registration for Your Business.
Chapter 3: Usage Restrictions and Permissions in Copyright Statements

1. Navigating Fair Use and Fair Dealing: Legal Boundaries Embedded in Copyright Statements
Fair Use et Fair Dealing represent crucial legal exceptions that inform usage restrictions and permissions referenced in copyright statements. These concepts define when limited use of copyrighted materials can occur without explicit authorization from rights holders, yet they operate distinctly based on jurisdiction and statutory frameworks.
In the United States, utilisation équitable is a flexible, case-specific doctrine permitting uses like criticism, commentary, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and research without prior approval. Its application hinges on assessing four core factors: the purpose of use, the nature of the original work, the amount used, and the effect on the work’s market value. This dynamic framework allows courts to balance creators’ rights with public interest on a situational basis, offering broader discretionary scope than many other systems.
Conversely, fair dealing governs copyright exceptions primarily within common law countries such as the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and Ireland. It offers a narrower, more defined set of permissible purposes—typically research, private study, criticism, review, and news reporting. Unlike fair use, fair dealing is not an inherent right but a defense against infringement claims requiring proper attribution in most cases. Its application depends on ensuring that the use neither conflicts with normal exploitation of the work nor unduly harms the author’s legitimate interests.
In copyright statements, these doctrines serve to clarify usage boundaries by signaling that certain unlicensed uses may be lawful under fair use or fair dealing defenses. However, neither grants an unconditional right to reproduce or distribute content freely. For example, making widespread copies or engaging in remixing often falls outside these exceptions unless additional licensing permits it. This nuanced interplay emphasizes that copyright statements must carefully communicate both the protections held by owners and the limited permissions users may exercise.
By embedding fair use or fair dealing considerations, copyright statements not only assert ownership but also guide lawful user conduct within recognized legal exceptions. This balance fosters respect for creators’ rights while accommodating appropriate public access for socially valuable purposes.
For a detailed comparative analysis of these exceptions, see the Irish library resource on copyright exceptions. To understand more about how copyright protection integrates with broader intellectual property concerns, visit our article on copyright protection for books, movies, and songs.
2. Harnessing Creative Commons Licenses: Balancing Permissions and Restrictions in Copyright Statements
Creative Commons (CC) licenses revolutionize how copyright statements communicate usage rights by shifting from the traditional “all rights reserved” approach to a more flexible “some rights reserved” framework. These licenses enable creators to grant clear permissions while retaining essential control over their works. Unlike conventional copyright, where access and use are limited without explicit authorization, CC licenses predefine allowed uses such as sharing, adapting, or commercial exploitation based on the chosen license type.
There are six principal CC license variants, each defining a distinct balance of permissions and restrictions. At the core, all require proper attribution to acknowledge the original creator. The CC BY license grants the broadest freedoms, permitting both commercial use and derivatives, only requiring credit. In contrast, CC BY-ND allows redistribution for commercial purposes but prohibits derivative works, preserving the original content’s integrity. NonCommercial licenses, like CC BY-NC and its variants, restrict usage to noncommercial contexts, often combined with ShareAlike terms that compel derivatives to carry the same licensing, fostering a sharing ecosystem with consistent terms.
This structured variety lets creators specify conditions that suit their goals—whether encouraging adaptation and growth of their work or limiting changes and commercial exploitation. Creators maintain legal ownership throughout, and licenses are non-exclusive, permitting concurrent or future alternations in licensing strategy.
For copyright statements, embedding the specific CC license signals not only ownership but the precise scope of permitted and restricted uses. This clarity reduces disputes and confusion for users, especially in digital and educational environments where open resources benefit from transparent licensing. However, it is critical to differentiate these licenses from the separate legal doctrine of fair use, which is situational and does not substitute for explicit permissions granted by CC licenses.
Through Creative Commons, copyright statements transform from static ownership declarations into dynamic tools of legal communication, specifying exactly what rights are granted or withheld. For a deeper understanding of copyright protections and how they interplay with usage restrictions, exploring foundational aspects in copyright protection for books, movies, and songs offers valuable insight.
More on Creative Commons licenses is available via their official resource at https://creativecommons.org/licenses/.
3. Navigating Public Domain and Government Works: Key to Usage Rights in Copyright Statements
A clear grasp of public domain materials and government works is essential when interpreting usage restrictions and permissions in copyright statements. Public domain works are those no longer protected by copyright, either because their copyright term has expired, they were never eligible, or the owner has relinquished rights. In the U.S., any work published before 1930 typically fits this category, making these creative expressions free for anyone to use, reproduce, and adapt without seeking permission. Government works hold a unique status under U.S. law; materials produced by federal employees as part of their official duties automatically enter the public domain. This legal standing means these works also carry no copyright restrictions, allowing unrestricted public use.
Determining the public domain status can be straightforward for older works but more complex for certain government-related materials. For instance, works created by contractors or third parties on behalf of the government may not automatically be free to use. This nuance often prompts copyright statements to explicitly declare a work’s status, providing crucial guidance to users regarding their rights and limitations. Unlike copyrighted works, which require explicit permissions to reproduce or adapt, public domain and government materials entail no such barriers, streamlining their usability.
While the fair use doctrine allows limited use of copyrighted content without permission for purposes like education or criticism, this framework does not restrict public domain or government works, which remain freely accessible for all applications. For creators and users alike, clearly noting whether a piece is public domain or government-produced within copyright statements aids in avoiding confusion and potential legal disputes.
Understanding these distinctions offers practical insight into copyright management and usage rights. For further details on identifying public domain status and government works, consulting resources like the Stanford Public Domain Flowchart is highly recommended.
Chapter 4: Copyright Statement Roles in Digital and Published Media

1. Integrating Technology and Legal Frameworks to Safeguard Copyright in Modern Media
Copyright statements function as vital legal beacons embedded within digital and published media, signaling ownership and defining permissible use. Technological advancements have enhanced these roles significantly. Tools such as digital watermarking invisibly encode ownership details within media files, making unauthorized duplication easier to detect. Plagiarism detection software scans vast content repositories to flag infringements, while metadata inclusion ensures that copyright information travels with digital files, preserving attribution across formats and platforms.
Legally, a copyright statement consists of the © symbol (or the word “Copyright”), the initial publication year, and the copyright owner’s name or recognizable abbreviation. This concise format clarifies the claim of rights and acts as a deterrent against infringement. In the digital realm, the enforcement of these rights is bolstered by legal structures like the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), which empowers copyright holders to request the removal of illegally posted content through takedown notices. However, because digital content flows globally, compliance with international agreements such as the Berne Convention requires careful navigation of varying jurisdictions.
Educational settings illustrate the nuanced balance between protection and access, where the TEACH Act permits authorized digital performances within certain strict conditions, reflecting copyright’s adaptability. Additionally, copyright statements often distinguish themselves from trademark and other intellectual property notices, emphasizing exclusive rights to the creative expression rather than branding elements.
Together, these technological aids and legal mechanisms transform the copyright statement into a comprehensive tool. It not only asserts ownership but enables actionable oversight, guiding lawful use and providing the foundation for enforcing rights across diverse media environments.
For deeper understanding of copyright frameworks, explore more about the basics of copyright law in business.
Reference: Digital Millennium Copyright Act
2. Economic Impact and Enforcement Challenges of Copyright Statements Across Media Platforms
Copyright statements serve as the linchpin in the economic and legal frameworks that protect creative works in both digital and traditional published media. By clearly declaring ownership and publication dates, these statements enable creators and rights holders to control and monetize their content effectively. In digital environments, especially where agency-produced assets are common, copyright ownership is often clarified through formal licensing agreements. These agreements specify the scope, duration, territorial reach, and residual rights, ensuring that economic exploitation is conducted transparently and reducing the risk of disputes or unauthorized use that could erode the work’s value.
The enforcement mechanisms tied to copyright statements address infringement through a multifaceted approach. Identification of unauthorized use is just the first step—rights holders must gather evidence sufficient for legal actions such as injunctions to halt violations, claims for damages, and obtaining court orders to disclose infringer identities. In traditional media, this process often involves direct legal proceedings and physical seizure of infringing goods. Digital platforms, on the other hand, primarily rely on takedown procedures grounded in laws like the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA). These platforms play a dual role as enforcers and gatekeepers, hosting reporting tools for infringements while managing counter-notifications to prevent wrongful removals, striking a delicate balance between protecting rights and preserving fair use, particularly for educational content.
Additionally, platforms must navigate evolving regulatory landscapes, exemplified by the EU Digital Services Act, which enforces transparency and mandates diligent management of repeat infringers. This layered enforcement ecosystem helps uphold the integrity of copyright ownership declared by statements, ensuring economic incentives remain aligned with legal protections. Understanding these economic and enforcement dimensions reveals how copyright statements do more than mark ownership—they actively facilitate lawful commerce and uphold creator rights in a highly dynamic media landscape.
For deeper insights, see external guidance on platform-based enforcement ethics under laws like the DMCA [1]. For more on harnessing copyright for commercial advantage, explore the benefits covered in [https://trademarkgold.com/benefits-of-copyright-business/].
3. Navigating Society and Global Power: The Far-Reaching Effects of Copyright Statements
Copyright statements play a critical role beyond merely marking ownership; they profoundly influence societal dynamics and geopolitical landscapes in today’s interconnected digital and published media. At a societal level, these statements protect creators’ rights, providing them with essential legal backing to monetize their work and spur innovation. This is especially vital for digital creators and influencers who depend on intellectual property rights to secure their content from misuse or impersonation, thus fostering a vibrant digital economy.
However, the enforcement of copyright statements can sometimes constrict free expression. Content filters, such as those mandated by regulations like the EU’s Copyright Directive, may unintentionally curb legitimate user-generated content including memes, parodies, and collaborative works. This tension underscores the challenge of balancing robust copyright protections with the freedom essential to creativity and open information sharing in digital communities.
Technological enforcement tools—plagiarism detection, digital watermarking, and DRM systems—have become indispensable for maintaining copyright integrity. While these tools help control unauthorized use, they also shape how audiences access and consume content globally.
On a geopolitical scale, copyright statements anchor international cooperation efforts to combat digital infringement and cybercrime. Global bodies like the United Nations and the International Telecommunication Union facilitate cybersecurity capacity building, particularly in developing regions, reflecting copyright’s role as a global digital asset safeguard. Yet, the complexity and cost of managing compliance tend to favor large multinational tech companies, concentrating market power and raising concerns over privacy and data control, which influence international digital power structures.
Moreover, copyright issues intersect with geopolitical conflicts and narratives in digital spaces, where control over media can affect political discourse and ideological battles seen in areas impacted by ongoing conflicts.
Overall, copyright statements are multifaceted tools that protect creative rights, shape cultural expression, and mediate global digital power, blending societal interests with international political realities. For deeper insight into legal copyright frameworks and their role in protecting creative works, see this detailed guide on copyright protection for books, movies, and songs.
For further understanding of their global impact and enforcement methods, refer to the United Nations’ ongoing international cybersecurity initiatives.
Chapter 5: Clarifying Ownership and Protection Status through Copyright Statements

1. Leveraging Technology to Strengthen Ownership Clarity and Protection in Copyright Statements
The technological foundation of copyright protection profoundly shapes how ownership and rights status are communicated through copyright statements. Copyright attaches automatically when a creator fixes an original work in a tangible form—be it digital code, written text, or visual art—instantly establishing legal ownership. However, this implicit protection benefits from augmentation through intentional public notices. Including a copyright statement containing the © symbol, the year of first publication, and the owner’s name clearly signals legal ownership, deterring unauthorized use by highlighting the protected nature of the work.
Beyond these notices, formal copyright registration elevates ownership clarity by creating an official record of a creator’s claim. This process, typically conducted through government offices, facilitates stronger enforcement in litigation by enabling claims for statutory damages and attorney’s fees. The submission of digital or physical copies during registration also timestamps and documents the work’s existence and ownership, providing a verifiable reference point.
In an increasingly digital landscape where content can be effortlessly shared and copied worldwide, technology-driven tools like digital watermarking and embedded metadata silently encode origin information into the work itself. Plagiarism detection software and online monitoring services automate the search for infringements, flagging unauthorized uses before they spread extensively. These tools assist creators in assembling robust evidence for enforcement actions, including time-stamped proof and usage logs.
Particularly for software, copyright law acknowledges automatic protection upon code creation, but registration enhances global legal strength thanks to international frameworks like the Berne Convention. Similarly, with emerging challenges such as AI-generated content where authorship must be human to qualify for protection, combining clear attribution and traditional copyright statements clarifies which elements are protected.
These technological safeguards collectively transform copyright statements into active instruments, not just passive labels, securing ownership while facilitating practical enforcement. For a deeper understanding of formal registration benefits and processes, see benefits of copyright registration in business.
For further insights on handling digital copyright protections, resources such as Aaron Hall’s guide on infringement detection offer valuable perspectives: https://aaronhall.com/how-to-handle-copyright-infringement-in-digital-content/
2. Economic Impact of Copyright Statements: Protecting Creative Industries and Encouraging Innovation
A clear copyright statement plays a crucial economic role by formally establishing ownership and the protection status of creative works. This transparency enables copyright holders to enforce their intellectual property rights effectively, which supports both revenue generation and the vitality of creative industries. By explicitly marking ownership, copyright statements help to deter unauthorized use and infringement, allowing creators and companies to monetize their works through licensing and sales. This monetization creates a direct income stream that sustains jobs and promotes economic growth within sectors heavily reliant on copyright protection.
The ability to license copyrighted content is particularly important in new, technology-driven markets such as artificial intelligence (AI). Here, clear ownership facilitates the lawful use of high-quality data sets for AI training, benefiting both copyright owners and developers. Conversely, unclear or ambiguous copyright status can lead to costly disputes and lost revenue. Globally, copyright infringement causes hundreds of billions of dollars in economic damage annually, highlighting the financial risks when ownership is not clearly communicated.
Though copyright protection encourages economic activity, it can also introduce inefficiencies, such as higher costs for consumers and potential restrictions on derivative creativity. Policymakers often face the challenge of balancing robust protections with fair access to foster innovation while preserving economic incentives.
Ultimately, copyright statements that clarify ownership and protection serve as essential tools to safeguard creative investment, reduce losses from unauthorized use, and maintain cultural and economic sovereignty. They ensure that creative industries have the legal and economic framework necessary to thrive in a competitive, digital marketplace.
For deeper insights into how copyright licensing supports economic growth amid evolving technologies, see the Copyright Alliance’s analysis on copyright licensing and AI’s economic impact. For more on protecting creative content in business contexts, explore this resource on copyright protection for books, movies, and songs.
3. Navigating the Legal Authority and Societal Impact of Copyright Statements
Copyright statements are more than just formalities; they serve as vital tools that bridge the legal framework of intellectual property with the societal respect for creative ownership. Legally, these statements act as explicit claims of ownership that alert users to the protected status of a work. By clearly displaying the © symbol, the year of first publication, and the name of the rightful owner, copyright statements establish reasonable notice, thereby reducing accidental infringements and reinforcing the enforceability of rights in disputes. This visibility encourages stronger legal enforcement, aiding actions such as DMCA takedown requests which help protect against unauthorized reproduction and distribution. Such practical enforcement mechanisms depend on the clarity and consistency of these copyright notices to uphold the owner’s interests effectively.
Beyond legal protection, copyright statements carry important societal weight. They endorse and promote respect for creators’ rights by signaling that the work is protected and must be used lawfully. This respect nurtures a culture where original content and creative industries can thrive economically and reputationally. Furthermore, clear copyright declarations build trust among creators, businesses, and consumers by demonstrating professionalism and a commitment to intellectual property integrity. This trust enhances credibility, reassuring stakeholders that creative assets and brand identity are conscientiously safeguarded. Consequently, copyright statements play a crucial role in cultivating a respectful creative environment, encouraging lawful usage, and supporting the economic viability of intellectual property.
Thus, copyright statements serve a dual purpose: they are indispensable legal tools for ownership assertion and enforcement, while also acting as societal signals that uphold the value and integrity of creative work. Their presence influences both the protection mechanisms of the law and the ethical engagement of users.
For an in-depth exploration of copyright notices and their role, see the comprehensive Wikipedia page on copyright notices. Additionally, understanding the benefits of copyright registration for business complements this perspective by highlighting how formal registration elevates legal protection and societal recognition.
Dernières réflexions
For business owners, understanding and effectively using copyright statements is essential to protect valuable creative assets and maintain legal control over their intellectual property. These statements not only assert ownership clearly through foundational elements but also communicate important legal information about protection duration, usage restrictions, and permissions. Applying them consistently across digital and published media ensures your content receives robust protection wherever it appears. Moreover, by clarifying ownership and the current protection status, copyright statements help prevent disputes, build trust, and empower your business to thrive confidently in a competitive marketplace. Taking the time to incorporate clear, accurate copyright statements will safeguard your brand’s originality and legal standing for years to come.
Obtenez votre marque dès aujourd'hui ! Des milliers de personnes ont protégé leur marque en déposant une marque. Qu'attendez-vous ? Commencez à déposer votre marque !
A propos de nous
The globe’s top website for registering trademarks and safeguarding your brand, name, logo, or slogan. We provide seamless, expert-led trademark registration services designed to protect your business identity and creative assets worldwide.